What Kind of Anesthesia is Used for a Root Canal?
Anesthesia in dentistry has been around for over 175 years. It has made root canal procedures safer and more comfortable. In the past, dentists used ether. Now, we focus on precise pain control and patient well-being.
Many patients worry about the anesthesia used in root canals. But, modern techniques use anesthetics that block pain signals. This lets dentists treat the infected pulp while keeping you relaxed. It shows our dedication to improving medical science and making dental visits less scary.
Key Takeaways
- Anesthesia in dentistry dates back more than 175 years.
- Root canal treatment removes infected pulp to alleviate pain.
- Modern anesthetics block pain signals during the procedure.
- Patient comfort is a priority in today’s dental practices.
- Sharing medical history helps tailor anesthesia choices.
Understanding Root Canal Procedures
Root canal therapy aims to remove infected pulp while keeping the natural tooth intact. It involves cleaning, disinfecting, and sealing the canal. This helps reduce pain and stops bacteria from spreading. Our focus is on making patients comfortable, using anesthesia for root canal.
What Is a Root Canal?
This procedure fixes damage that goes into the tooth’s internal chamber. Doctors usually suggest it when pulp tissues show signs of serious inflammation or infection. By removing these tissues, they help keep the tooth strong.
When Is a Root Canal Necessary?
Deep cavities or cracks that reach the pulp often need this treatment. If left untreated, infection can cause abscesses around the roots. Early signs include a throbbing toothache and sensitivity to hot or cold foods.
Common Symptoms Requiring Treatment
- Prolonged pain after eating or drinking
- Dark discoloration of the tooth
- Heightened tenderness in the gums
| Key Concern | Notable Detail |
|---|---|
| Inflamed Pulp | Causes persistent discomfort |
| Deep Infection | May require anesthesia for root canal |
Types of Anesthesia for Dental Procedures
Many wonder how they stay comfortable during dental treatments. There are three main ways to manage pain: local anesthesia, sedation, and general anesthesia. Each method is used for different treatments and patient needs.
What Is Local Anesthesia?
This method numbs a specific area but keeps you awake. Drugs like Lidocaine or Novocain stop pain by blocking nerves. You can talk to your dentist without feeling pain.
Overview of Sedation Dentistry
Sedation relaxes you and reduces fear. It can be taken by mouth or through an IV. It makes you feel sleepy but you can follow instructions.
General Anesthesia Considerations
General anesthesia makes you deeply asleep. It’s used for complex procedures or when you’re very anxious. Doctors watch your vital signs to keep you safe.
| Anesthesia Type | Consciousness Level | Usage | Example Agents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Anesthesia | Fully Awake | Routine Dental Work | Lidocaine, Novocain |
| Sedation Dentistry | Minimized Awareness | Moderate Procedures | Midazolam, Diazepam |
| General Anesthesia | Fully Unconscious | Complex Interventions | Propofol, Ketamine |
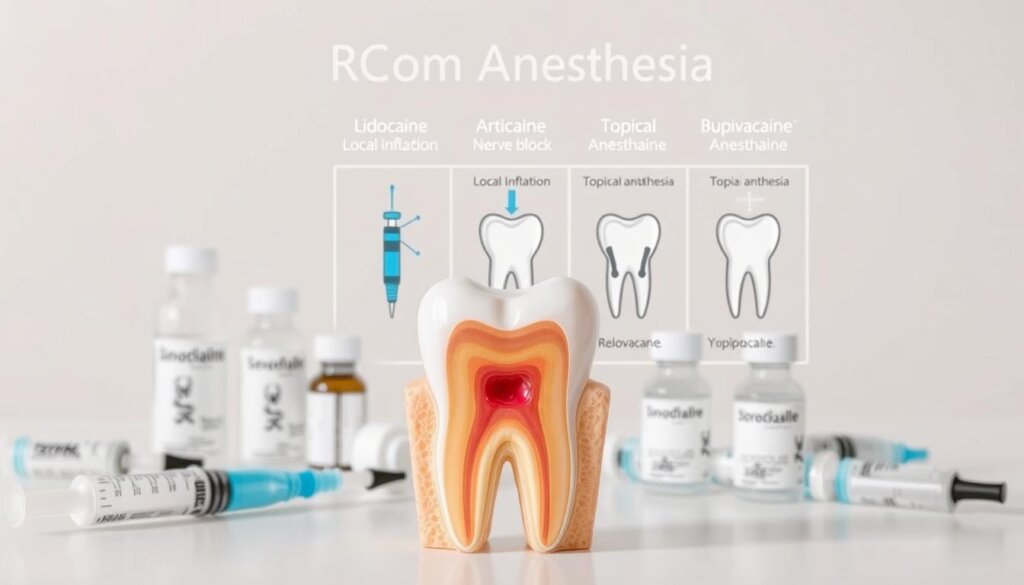
Local Anesthesia in Root Canals
Local anesthesia for root canals makes patients calm and focused on healing. It targets specific nerves to reduce pain and improve treatment precision. This method helps dental teams achieve better results while caring for patient well-being.
Popular Local Anesthetics Used
Lidocaine (with epinephrine), articaine, and mepivacaine are top choices. They are known for their reliable effects and low risk of systemic problems. Lidocaine is often preferred due to its widespread use. Articaine might work better in bone, while mepivacaine is good for those allergic to certain additives.
Mechanism of Action of Local Anesthetics
These drugs block nerve signals by stopping sodium-channel activity. This action reduces pain signals, making the procedure more comfortable. It allows for precise endodontic work.
Duration of Effectiveness
Numbness usually lasts one to three hours. Adding epinephrine can extend this time, keeping the area stable. The choice depends on the patient’s health and how long the anesthesia is needed. Local anesthesia is key in modern dental care, ensuring thorough treatment without too much pain.
Sedation Options for Root Canals
Many people feel stressed about complex dental procedures. Sedation helps by making them feel more at ease. It works with numbing to make sure patients are comfortable during root canals.
Mild Sedation Techniques
Oral sedatives can calm those who are nervous about dental visits. Nitrous oxide inhalation is another gentle option. Both keep patients able to answer questions and follow directions.
Moderate Sedation for Anxious Patients
Moderate sedation uses intravenous medication for deeper relaxation. It’s for those with severe anxiety. The dentist will watch your vital signs closely and use numbing to ensure comfort.
Deep Sedation and General Anesthesia
Deep sedation and general anesthesia make patients almost or fully asleep. They’re used for tough cases or extreme anxiety. Experts will watch your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing.
| Sedation Level | Delivery Method | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | Oral sedative / Nitrous oxide | Reduces mild anxiety while keeping patient responsive |
| Moderate | Intravenous (IV) | Decreases deeper fears and allows steady cooperation |
| Deep / General Anesthesia | IV / Inhalation agents | Provides maximal relaxation for lengthy or complex procedures |
The Role of Nitrous Oxide
Many dentists use nitrous oxide to make procedures more comfortable. This gas, known as laughing gas, helps patients relax during treatments. It keeps them awake but calm. The effects wear off quickly, and the dosage can be changed anytime.
Benefits of Nitrous Oxide in Dentistry
- Quick onset with immediate relaxation
- Adjustable sedation level for personalized comfort
- Lower risk compared to deeper anesthesia methods
Patients feel relaxed but stay alert. This helps them communicate during the treatment.
How Nitrous Oxide Is Administered
Dentists use a small mask to give a mix of nitrous oxide and oxygen. They can change the sedation level as needed. This makes sure each patient gets the right amount of comfort.
Risks and Considerations
Some people might feel a bit nauseous if they haven’t eaten. Those with breathing problems or long-term health issues should talk to their dentist first. Many choose nitrous oxide for root canals because it’s safe and they recover quickly.
Preparing for Anesthesia during a Root Canal
Patients get clear guidelines for dental anesthesia options during a root canal. A good start is talking about sedation choices and health. This talk helps find the safest option for each person.
Pre-Procedure Instructions
Dentists give specific steps before you go. Some might need to skip meals or drinks for a while. This helps avoid risks with sedation. Steps include:
- Following fasting times
- Confirming medication schedules
- Arranging transportation for deeper sedation
Discussing Medical History with the Dentist
Telling your dentist about health issues or past reactions to anesthesia is key. A full check of heart, lungs, current meds, and allergies is important. This helps make a plan that’s safe and comfortable for you.
| Guideline | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Fasting Period | Reduces risk of nausea |
| Allergy Disclosure | Prevents adverse reactions |
| Medication Review | Ensures safe sedation plan |
Post-Procedure Anesthesia Effects
Numbness can last a short time after the anesthetic fades. You might feel slight tingling and mild dryness around your lips or tongue. But, most people get back to normal feeling quickly.
Some people might feel a bit lightheaded for a short while. How long this lasts can depend on the type of anesthetic used, like the best one for root canals.
Common Side Effects of Anesthesia
Minor soreness at the injection site is common. Some people might feel a bit nauseous or have an upset stomach. A small number could have an allergic reaction, so watch for swelling or ongoing pain.
But, these effects are rare when the best anesthesia for root canals is used.
Managing Discomfort After the Procedure
Here are some ways to help:
- Use gentle over-the-counter pain relievers if advised
- Drink water to fight dryness
- Rest until you feel fully alert again
FAQs about Root Canal Anesthesia
Many people wonder about the comfort and safety of dental treatments. Modern dentistry uses careful protocols and anesthetic techniques for root canals to reduce pain. Success often depends on how well the body responds and the method used during the injection.
Is Root Canal Anesthesia Painful?
Modern numbing methods, like using topical gel before the needle, make injections less painful. Dentists use thin needles and slow injection to lessen pain. This approach helps patients feel more at ease.
How Long Does Anesthesia Last After a Root Canal?
The numbness usually lasts from one to three hours. But, it can vary based on the anesthetic used. Some anesthetics have vasoconstrictors to make the effect last longer, ensuring pain relief during the procedure.
Can I Drive After a Root Canal?
Mild sedation usually lets you drive safely. But, deeper sedation means you should have someone with you. The dosage and how you react to it will decide if you can drive after.
| Sedation Type | Typical Experience | Driving Suggestion |
|---|---|---|
| Local Anesthesia | Patient remains fully awake | Safe to drive |
| Mild Sedation | Relaxed but conscious | Usually safe to drive |
| Deep Sedation | Limited awareness | Arrange a ride |
Choosing the Right Anesthesia for You
Every root canal needs a plan that makes you comfortable and safe. Some people feel a little nervous, while others worry more about their health. The right anesthetic makes the treatment smoother and reduces stress.
Factors Influencing Anesthesia Choice
Your personal situation plays a big role in choosing anesthesia. Your health, like heart problems or pregnancy, affects the choice. Also, if you’ve had dental fears or issues before, it matters.
- Underlying medical diagnoses
- History of heightened anxiety
- Special needs or requirements
Doctors look at these factors to suggest local anesthetics or sedation. This tailored approach ensures you feel safe before, during, and after the root canal.
Consulting with Your Dentist
Talking to a dentist you trust can help find the best option. They consider your treatment, answer your questions, and make sure the anesthetic fits your needs. This conversation builds confidence and makes the experience more relaxed.
Cost Considerations for Anesthesia
Root canal procedures usually include basic anesthesia in the overall fee. Sedation costs can vary based on the type of practice and sedation level. Some patients look for ways to manage costs without sacrificing comfort.
Average Costs for Anesthesia in Root Canals
Fees can range from small additions for minimal sedation to higher charges for general anesthesia. Local anesthesia is often included in the standard price. Deep sedation or intravenous methods can increase the total cost.
Factors like location, clinic setting, and equipment needed also affect costs.
Insurance Coverage for Dental Anesthesia
Many insurance providers offer partial or full coverage for dental anesthesia. It’s important to confirm coverage before treatment to avoid unexpected bills. Even with coverage, some procedures might need pre-authorization.
Clear communication with the dental office and insurance provider is key. It ensures financial transparency and a well-informed treatment plan.
Alternatives to Traditional Anesthesia
Some people look for ways other than usual numbing shots. They want gentler methods to help with anxiety and pain during dental visits. This choice is for those who prefer natural or advanced options, based on their needs or how sensitive they are.
Herbal and Natural Sedatives
Some patients talk about using chamomile or valerian to relax before dental work. These herbs might help calm nerves but don’t block pain well. It’s important to talk to a doctor before trying these, as the right amount and any side effects need to be checked.
Technology Innovations in Dental Anesthesia
New tech like computer-controlled local anesthetic systems, like The Wand, is being used. It makes sure the right amount is given. Also, needle-free injectors are being tested for those who really hate needles. These tools are not everywhere yet, but they show how dentistry is trying to make visits more comfortable.
Patient Testimonies and Experiences
Many people fear discomfort and avoid going to the dentist. They worry about the pain of a root canal anesthesia and possible side effects from sedation. But, new methods make the experience controlled and comfortable.
Common Concerns Related to Anesthesia
People often worry about the pain of injections or numbness that lasts too long. They’re unsure how they’ll react to sedatives. Dentists listen to their concerns, review their medical history, and explain each step. This makes patients feel ready and calm.
Positive Experiences with Root Canal Anesthesia
Many patients say they were relieved when the procedure ended without the pain they feared. Those who used sedation felt less anxious the whole time. These stories help dental teams understand and meet each patient’s needs.
Research and Studies on Dental Anesthesia
Scientists are working on new agents to make dental anesthesia safer and more comfortable. They’re looking at ways to improve nerve-blocking to better reach the bone. This could help with complex dental work and reduce risks.
Recent Advances in Anesthesia Techniques
New anesthetics are being developed to last longer and target specific nerves. These studies show they can reduce swelling and help patients recover faster. Experts say better monitoring of sedation is key to avoiding problems.
Future Trends in Anesthesia for Dental Procedures
Personalized care is on the horizon for dental treatments. Research suggests genetic testing could match anesthesia to each person’s needs. This could lead to more accurate treatments and fewer mistakes.
| Technique | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prolonged-Acting Agents | Extended pain relief, fewer reinjections |
| Central-Acting Sedation | Reduced anxiety during lengthy procedures |
| Biologic Monitoring | Customized dosage with decreased side effects |
Conclusion on Anesthesia for Root Canals
Modern anesthesia has made root canal treatments safer. It helps manage pain and builds trust with patients. Many times, these methods make the procedure almost painless and save the natural tooth.
Recap of Important Anesthesia Information
Dental anesthesia includes many choices, from local injections to deeper sedation. Each choice depends on the patient’s medical history and comfort level. Talking openly with dental professionals helps understand possible side effects and outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Patient Comfort and Anesthesia
Root canal anesthesia aims for a positive experience. Good communication and preparation can reduce anxiety. As research grows, more sedation options will be available, tailoring care for each patient’s needs.